Clients that use WiFi can experience a number of issues that can affect the speed and performance of a wireless network. Below, we have listed out a variety of simple tests that give users a basic look at client health. While additional tests may be needed to fully troubleshoot an issue, the following tests are a great starting point.
RSSI / Signal Strength
Received signal strength (RSSI) is the power of the AP’s signal as it reaches the device (mobile phone, laptop, etc.).
2nd Access Point Coverage
Second access point (AP) coverage allows users to roam from AP to AP without losing significant signal. This means that there is no interruption to the connection when the device is switching to the next closest AP.
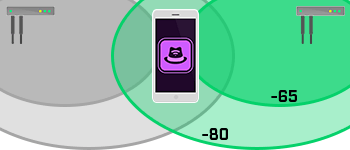
3rd Access Point Coverage
Third access point (AP) coverage ensures that at least three different APs can see a device. That allows for triangulation of devices location.
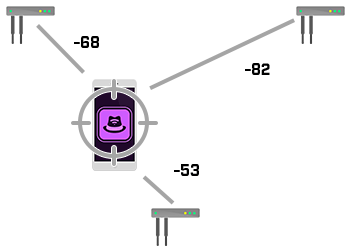
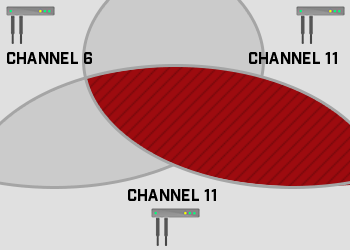
Co-Channel Interference
Co-channel interference, or channel overlap, is concerned with the efficiency of the network design. If two or more adjoining APs are on the same channel frequency, this can cause interference issues that drastically effect performance.
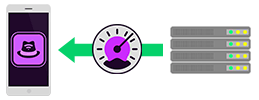
Download
Downloading a file from a server is a standard bandwidth test used to test the speed of the network’s connection. This can be done both locally and over the internet.
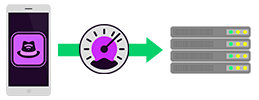
Upload
Uploading a file from a server is a standard bandwidth test used to test the speed of the network’s connection. This can be done both locally and over the internet.
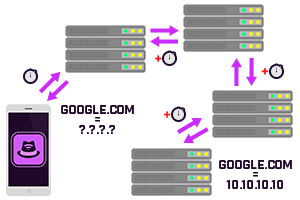
DNS
Domain Name Servers (DNS) act as translators for URLs and IP addresses. A person types in a URL (ex: google.com), then a request is sent to a DNS to pull the IP address that correlates with that URL. This allows users to type in named URLs instead of IP addresses to get to a particular website.
This test shows the time it takes for that request to go through.
Round Trip Time (RTT)
Round Trip Time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a device to connect to a server and get an acknowledgement back.
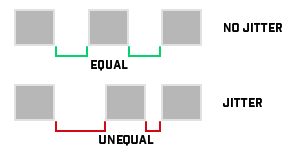
Jitter
Jitter is a variation in packet transit delay caused by queuing, contention and serialization effects on the path through the network.
Packet Loss
Packet loss tests how many, if any, packets are loss during transmission.

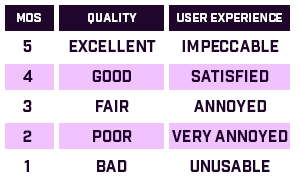
MOS Score
Mean Opinion Score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering, representing overall quality of a stimulus or system.